From “Star Trek’s” Holodeck to Tony Stark’s JARVIS in “Iron Man,” the idea of artificial intelligence creating intellectual value has been a staple of science fiction for decades. In today’s article, we take a closer look at generative AI tools that make those visions a reality.
The current wave of generative AI tools are smart, capable, and learning new tricks at a pace humans can’t compete with. They can “paint” impressive digital images in the style of Monet and write poetry in the voices of Whitman or Dickinson, all based on simple prompts.
But how exactly do they work and how can you make the most of technology?
Here’s everything you need to know. 👇
🤖 Understanding Generative AI
It feels like it’s been ages since ChatGPT’s launch. But OpenAI’s crown jewel and one of the first mainstream generative AI tools was released less than a year ago. Since then, we’ve seen the new generation of AI-powered tools seep into the public attention.
So, what exactly is generative AI?
In a nutshell, generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence and an umbrella term for a variety of machine learning (ML) methods and technologies designed to generate content. Generative AI can write code, generate stunning digital art, engage in eerily human-like conversations, create videos, record music, and even simulate speech.

In a way, you can think of generative AI as a skilled impersonator that can learn from a famous actor’s style and mannerisms, down to the finest details. Except, a generative AI model can show similarly impressive performance in almost every aspect of creative work.
Interacting with generative AI tools like ChatGPT usually happens via prompts which are essentially sets of instructions written in natural language. They can be as simple as:
“Generate an image of a unicorn slipping on a banana peel.”
or as complex as:
“Create a detailed outline for a dystopian novel where a rogue AI takes control of all digital systems, causes global chaos, and destroys the last pockets of human resistance.”
(let’s hope this ages better than most internet memes)
Writing good prompts can be tricky and usually requires a lot of follow-up prompts to refine the output. As unsettling as it may sound, it’s an inherently collaborative process that combines human creativity and the computational capabilities of generative AI.
What’s Under the Hood of Generative AI?
Since this is merely an introduction to generative AI, we won’t be getting into the technical nitty-gritty today. But there are three key technologies driving generative AI you should know.
First are Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). These machine learning systems use two neural networks — a system of algorithms mimicking the human brain’s function — one responsible for generating new data and the another for evaluating how realistic it is.
Next are Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), another type of machine learning systems that generate data similar to the training data the AI was fed during training. VAEs can be used for generating images, detecting unusual patterns, and reducing the complexity of data.
Finally, transformer models like GPT-3 or GPT-4 — the large language models (LLMs) powering ChatGPT — are used for generating and processing human-like text.
All three methods are designed to generate new data and have the ability to learn from existing datasets — think online conversations or collections of fine art — to improve their output. They can also be used individually or in combination within complex AI systems.
🚀 The Evolution of Generative AI
Legacy AI tools like the 1970s MYCIN(1) designed to aid diagnosis of bacterial infections or ELIZA(2), the first chatbot, were crude systems that relied on sets of predefined rules.
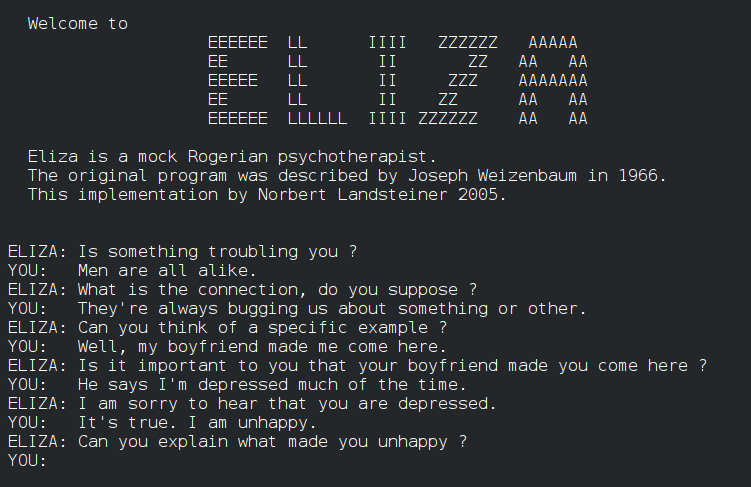
It wasn’t until the 2000s that deep learning — the use of neural networks to recognize and learn complex patterns — became a thing. It was possible thanks to the sheer amount of data floating around online and the advancements in computing power and algorithms.
In 2013, Diederik Kingma and Max Welling proposed Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), a generative modeling framework.(3) In the following year, Ian Goodfellow and his team introduced Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), a next milestone for generative models.(4)
The 2010s sparked more interesting developments in the field, including Google’s DeepDream, a combination of neural networks that could generate psychedelic and surrealistic images.(5)
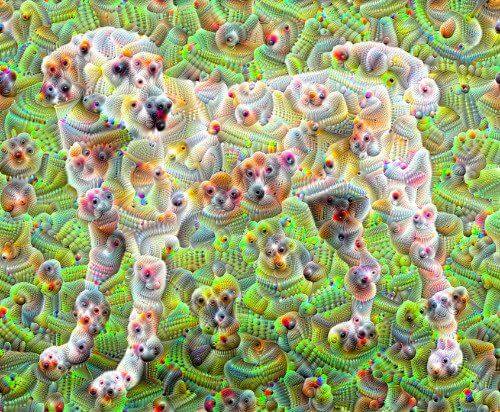

The field of generative AI was still in its infancy, but the breakthrough in image generation opened the door to further progress. In 2016, DeepMind developed a deep generative model WaveNet for speech and audio synthesis, the first to deliver natural-sounding speech.(6) A year later, a team at Google Research published a paper titled “Attention is All You Need” that introduced the transformer architecture. And this is where things got interesting.(7)
Over the next two years, transformer architecture became a dominant force in AI research. OpenAI spearheaded the development of GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models, and Google launched BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers).(8)
In 2019, OpenAI introduced GPT-2, a large language model trained on 8 million web pages. It was the first large-scale transformer model that showed what generative AI is capable of in terms of understanding and generating coherent, contextually-relevant text.(9)
Last year, we also saw the emergence of a new generation of text-to-image diffusion models like Midjourney, Stable Difusion, and DALL-E 2. Together with OpenAI’s GPT-3 and GPT-4, they are currently the most popular and powerful generative models available to the public.
🕹️ Applications of Generative AI
Content Creation
Text, sound, visual arts… even domains that would traditionally require ingenuity, artistic expression, and deep context comprehension have been impacted by artificial intelligence.
AI tools like Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, or DALLE-2 can create marketing collaterals, social media content, logos, or photo-realistic images. Transformer models write articles that are often indistinguishable from human-written text, all based on natural-language prompts.
Generative AI can even compose music that tops the charts, well, kind of.
Earlier this year, a song titled “Heart on My Sleeve” featuring vocals that were believed to be by Drake and The Weeknd went viral on social media. The song turned out to be fully AI-generated and was later removed from streaming services after scoring millions of listens.
Healthcare
No more waiting for appointments or dealing with pesky co-pays, because why bother with actual human expertise when you can rely on algorithms and data?
From medical imaging and diagnosis to drug discovery, patient monitoring, personalized medicine, and even customer care through chatbots, generative AI can do it all.
While we’re some time away from robots replacing doctors and nurses, LLMs are getting close to being useful in the field. According to Dr. Isaac Kohane, a physician and a computer scientist at Harvard, GPT-4 can already rival some doctors in medical judgment.(10)
A paper by researchers at Microsoft and OpenAI shows that the latest GPT model shows a 30% improvement over GPT-3 on USMLE (standardized medical examination) questions. It even managed to achieve a 60 percent passing score in multiple-choice questions.(11)
Game Development
The human brain is hard-wired for novelty and surprise. That’s why you can’t resist a good old loot box in your favorite video game or get so excited for a plot twist you didn’t see coming.
The entertainment industry has relied on this mechanism for decades. Game developers have been using procedural generation to create terrain, levels, objects, and characters. Games like Minecraft and No Man’s Sky used this technique to create entire worlds teeming with life.
While procedural generation relies on mathematical formulas and logic-based rules, generative AI uses machine learning models and neural networks to generate new content.
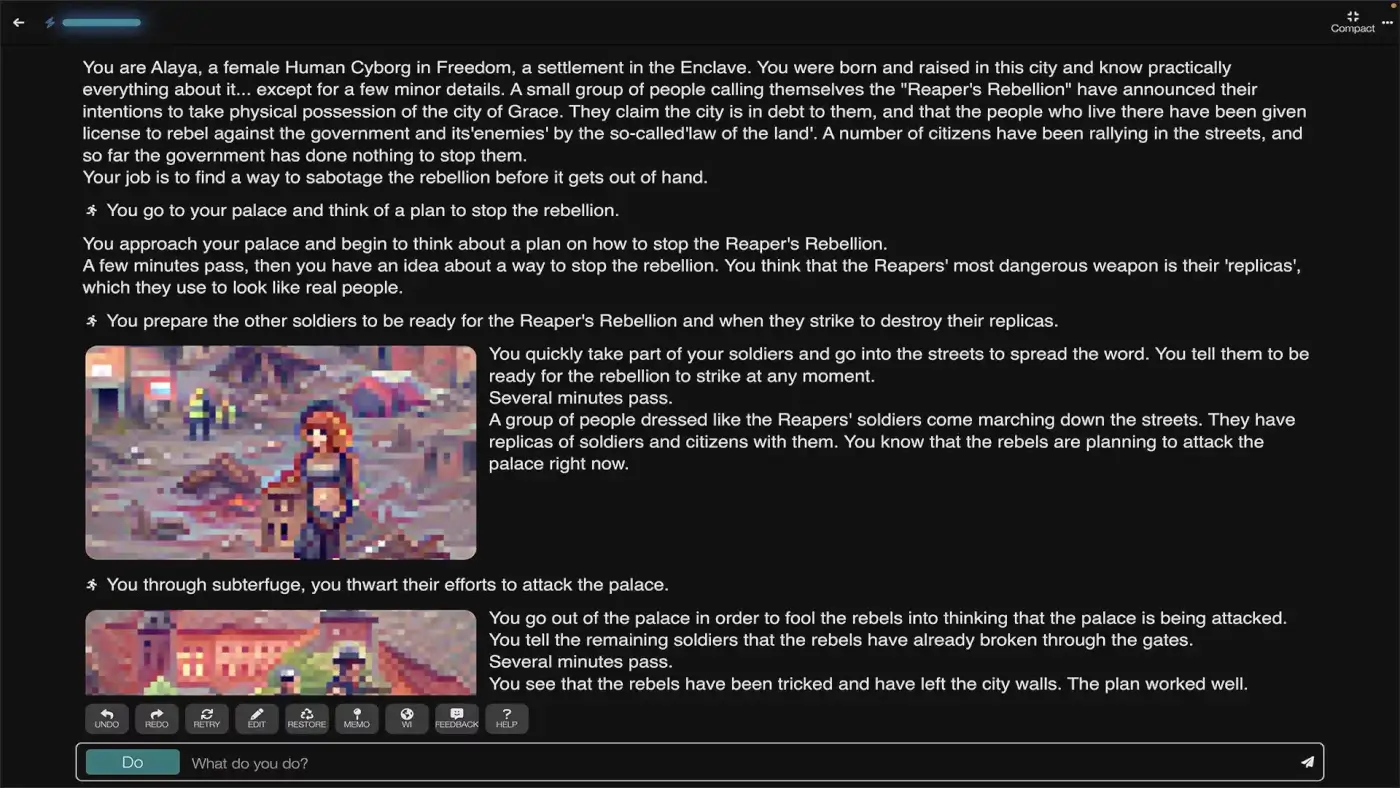
Image credit: Latitude via Steam
Major gaming studios are adopting generative AI for creating animations, voice synthesis, sound effects, textures, 3d and 2d objects, and even dialogue lines for NPC characters.
Some are using generative AI in even more ingenious ways. An AR engineer Dan Dangong managed to feed the source code of the classic Game Boy Advance game Pokémon Emerald into ChatGPT and turn it into a text adventure. Pretty cool, huh?(12)
Software Development
Tools like GitHub’s CoPilot — a code-autocompletion tool doubling as a programming buddy — have become a staple in a coder’s toolbox, both among new and seasoned programmers.
AI-powered tools help developers speed up writing code, streamline debugging, and even democratize programming by making it accessible to those without a technical background.
According to a GitHub survey, the use of generative AI and code-autocompletion tools in software development speeds up coding by as much as 9.3%. This is nothing to sneeze at, especially considering the rapid growth of LLMs and increasing automation of coding tasks.(13)
🔮 The Future of Generative AI
Generative AI is rapidly transforming from “that fancy tech thing” to a powerful, creative tool nobody can afford not to use. The question is where do we go from here?
As powerful as they are, even the most powerful large language models still have many limitations like a degree of bias inherited from the training data and a tendency to hallucinate (read: make stuff up). The cost of training and maintaining the models is another obstacle.
Luckily, there are alternatives.
In February 2023, Mark Zuckerberg’s Meta released the first open large language model LLaMA. The goal was simple — to “help researchers advance their work in this subfield of AI.” LLaMA has since spawned a number of open-source models like Stanford’s Alpaca 7B,
The dawn of open-source models is a step toward democratization of AI. The access to lightweight tools gives tech-savvy users a chance to develop their own AI-based tools without having to invest in commercial-grade, expensive hardware.
But interfacing with powerful generative AI is still a challenge — writing good prompts and follow-ups is harder than it seems. While conversational AI tools like ChatGPT are going to play a major role, task automation via agents may streamline AI workflows even more.
In a nutshell, AI agents or autonomous agents are small applications that “communicate” with existing language models like GPT-3 or GPT-4 to automate complex tasks. They can write code, build websites, search the web, or… starting a business with a single prompt.
The code is straightforward:
— Sully (@SullyOmarr) April 11, 2023
We start with a goal eg: "Solve world hunger"
We tell GPT4 "In order to solve world hunger, how can we create simpler tasks?"
Then it's able to figure out what to do on its own, and runs until all the task are completed. pic.twitter.com/oYE9TH45gS
We’re not at the point where AI models have evolved enough to understand and carry out complex tasks with full autonomy. But AI agents like Auto-GPT or BabyAI open an interesting avenue to explore for generative AI to explore in the coming years.
Want to learn more about AI agents?
Read our article on autonomous task management next!
💭 Embracing the AI Revolution: Final Thoughts on the Power and Potential of Generative AI
At this point, nobody knows how the ongoing AI revolution will shape the world in the coming years. But it’s clear that it’s already changing the way we work, create, and innovate.
Whether you want to use generative AI to automate repetitive, low-value tasks or as a trusty sidekick for all things creative, there is tremendous value in embracing this technology.
Before you go, here’s a quick recap of everything we learned today:
- Generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence that uses machine learning methods to generate content such as text, images, videos, and music.
- Key technologies driving generative AI include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and transformer models like GPT-4.
- Generative AI tools can be used in content creation, healthcare, art and design, game development, fashion, architecture, and customer service.
- Some of the most popular and powerful AI-based tools available today include Midjourney, Stable Difusion, ChatGPT, and DALLE-2, just to name a few.
And that’s it!
As you’re navigating this new AI-powered landscape, Taskade AI can help you work smarter, streamline project workflows, and supercharge task management.
🤖 Custom AI Agents: Develop AI agents that take the capabilities of generative AI to the next level, from content creation to problem-solving.
🪄 AI Generator: Explore the creative potential of generative AI — describe what you’re working on and receiving unique projects and documents.
✏️ AI Assistant: Use powerful /AI commands in the project editor to generate content, edit text, and manage your tasks faster and smarter.
🗂️ AI Prompt Templates Library: Dive into a collection of AI prompts designed to help you make the most of Taskade’s generative AI tools.
And much more…
Be sure to check some of our AI resources before you go.
- 🤖 Grab AI generators for business and personal projects
- 📥 Download Taskade’s AI app for desktop and mobile
- ⏩ Read the history of OpenAI’s ChatGPT
Frequently Asked Questions About Generative AI
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that mimics the cognitive abilities of humans, essentially leveraging the power of machine learning algorithms to generate content such as text, images, music, and more. It enables computers to learn patterns and generate similar yet novel output by themselves, making it a major cornerstone in modern AI advancements.
How Does Generative AI Create Images?
Generative AI creates images by harnessing neural networks such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). These networks comprise two parts: the generator, which creates the images, and the discriminator, which critiques the images based on a real dataset. Over time, the generator learns to improve its outputs to make them more realistic and believable, enabling the production of high-quality, AI-generated images.
What’s the Difference Between AI and Generative AI?
While AI, or Artificial Intelligence, represents the broad discipline of machines simulating human intelligence, Generative AI is a specific branch within this field. AI includes a wide range of technologies, such as image recognition, natural language processing, robotics, etc. In contrast, Generative AI focuses on creating new content or predicting new outcomes based on the learned patterns and data inputs.
What is the Most Popular Generative AI?
OpenAI’s GPT-4, and by extension ChatGPT, are arguably one of the most popular generative AI tools available today. It can be used to generate human-like text and has applications across various fields, from drafting emails to creating written content and coding. GPT-4’s ability to generate high-quality text has made it a benchmark in the world of generative AI.
Is Generative AI Free?
While some models and APIs, such as GPT-2 by OpenAI, can be accessed for free, others require a subscription or payment for their use. Many AI research organizations and companies provide free or low-cost access to their models for non-commercial use. Unless you can run open-source AI models on your own devices, commercial usage typically involves a cost.
🔗 Resources
- https://www.britannica.com/technology/MYCIN
- https://www.vox.com/future-perfect/23617185/ai-chatbots-eliza-chatgpt-bing-sydney-artificial-intelligence-history
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1906.02691.pdf
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661
- https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/generative/deepdream?hl=pl
- https://www.deepmind.com/research/highlighted-research/wavenet
- https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
- https://blog.google/products/search/search-language-understanding-bert/
- https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/openai-assets/research-covers/language-unsupervised/language_understanding_paper.pdf
- https://www.insider.com/chatgpt-passes-medical-exam-diagnoses-rare-condition-2023-4
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.13375.pdf
- https://www.polygon.com/23643321/chatgpt-4-ai-pokemon-emerald
- https://github.blog/2023-06-13-survey-reveals-ais-impact-on-the-developer-experience/


 Agentic AI Systems — The Next Evolution of Work
Agentic AI Systems — The Next Evolution of Work  AI Agent Builders: Empowering A World of Automation
AI Agent Builders: Empowering A World of Automation  How To Humanize AI Generated Content — Build An AI Agent That Does It For You
How To Humanize AI Generated Content — Build An AI Agent That Does It For You  From Distraction to Action: AI For ADHD Productivity
From Distraction to Action: AI For ADHD Productivity  12 Best AI Tools for Coding
12 Best AI Tools for Coding  Top 10 AI Influencers to Watch in 2024
Top 10 AI Influencers to Watch in 2024